

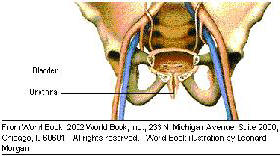
Male urethra (urethra masculina)
The urethra, a tube approx. 20 - 25 cm (8 - 10 in) in length and lined with mucous membrane, serves the excretion of urine and sperm. It originates at the bladder (vesica urinari) and punctures the prostate gland approx. 3 cm further along.
At this point it is joined by the excretory tracts of the spermatic duct (ductus deferens) and the reproductive glands.
A short section passing through the pelvic floor follows. From here on, the longest section begins, surrounded by the cavernous bodies of the penis (corpus cavernosum penis) and the spongious bodies of the penis (corpus spongiosum penis) running through the male penis and ultimately ending in the external urethral aperture.
The section located shortly before the urethra enters the male penis is surrounded by muscle fiber, forming the urethral sphincter muscle.
Female urethra (urethra feminina)
The female urethra originates at the bladder (vesica urinaria), crosses the pelvic floor and ends in the vaginal vestibul (vestibulum vaginae) below the clitoris.
In contrast to the male urethra (urethra masculina), it is only 3 - 4 cm (1.2 - 1.6 in) long.
Urinary System