

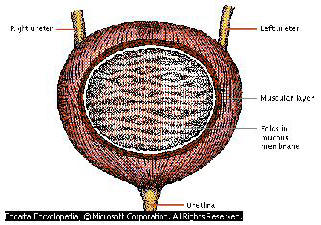
The urine excreted by the kidneys is collected in the bladder. It has a volume of approx. 500 ml (0.1 gal), whereby the maximum capacity can vary quite a lot, depending on individual training. A desire to urinate occurs at approx. 200 ml (0.04 gal).
When full, the bladder is spherical, when empty like a loose sack. It can be divided up into four sections:
|
the tip or parting of the bladder, connecting it to the navel | |
|
the body of the bladder, constituting the largest part of the bladder wall | |
|
the base of the bladder, more or less constituting its 'floor' | |
|
the neck of the bladder, constituting the entrance to the bladder |
The tip of the bladder, as well as the posterior and lateral parts of the body of the bladder are covered with peritoneum.
The bladder is emptied in a manner essentially controlled by the sphincter muscle of the urethra. Paralysis of the urethra leads to incontinence.
Urinary System